
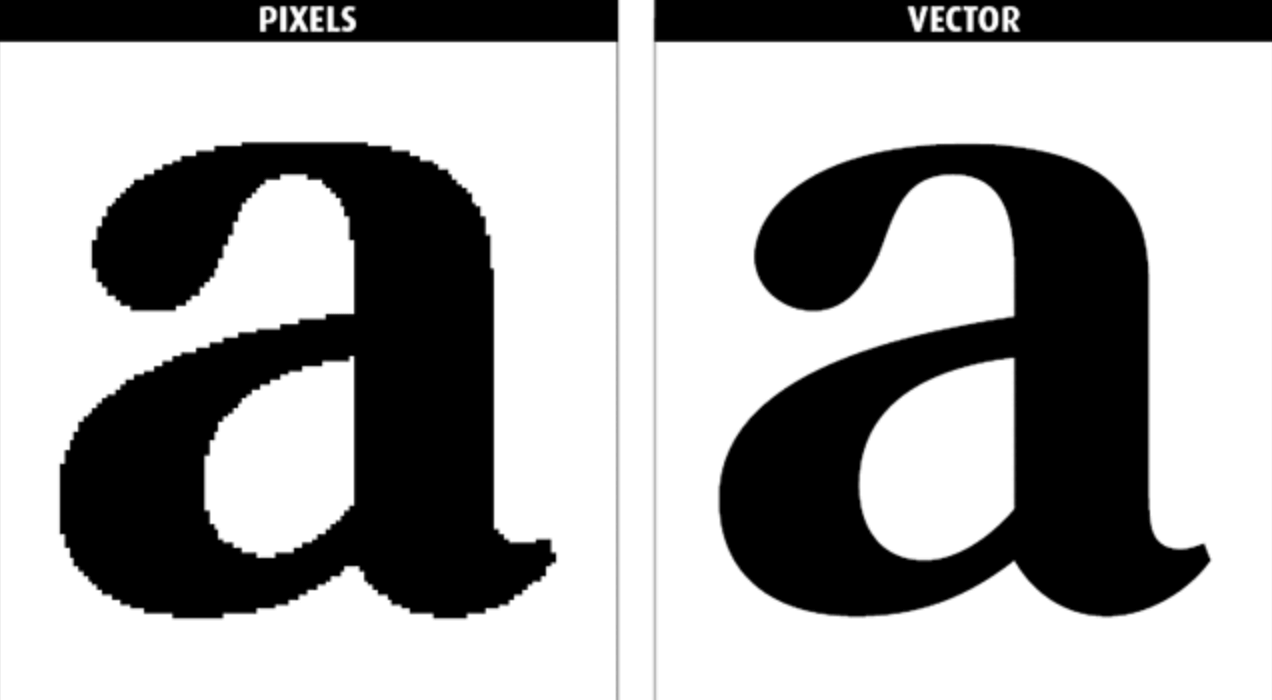
For maximum quality, TIFF is a good choice. For example, if the file needs to be high quality but very small, JPEG is good. In addition, there are real differences among the formats (see the chart above) and some formats really are better for certain applications.

Other users and developers, of course, do not wish to submit to this and so they develop their own formats. Some file format developers (such as CompuServe with GIF) try to maintain some level of control over their formats. There are many reasons for this but the primary ones are money and practicality. Why are there so many different image file formats? There are many other differences between file formats but most of them are not important for the average user to know about. How much loss there is depends on your choice of image compression level and on the nature of the image you are compressing. If you convert an image from RGB to JPEG and back to RGB, you will lose some level of quality in the transition to JPEG and can never get it back. This means that, unlike the PPM, RGB and PNG files which are totally equivalent, the JPEG file is not.
RASTER FILES FULL
Finally, the JPEG image (.jpg) is the smallest image and is a full 24 bit color image but it is compressed using a lossy compression scheme. The PostScript (.ps) file is unusual because it is not a raster image at all but rather a vector image (see the discussion on PostScript files). The PPM file is uncompressed and therefore very large and is of absolutely equivalent quality to the PNG image which is less than a fortieth of its size. The GIF file has only 8 bit color and is therefore basically of lesser quality than the other images (of course it is also smaller and on an 8 bit color monitor would be just as good as a 24 bit color image). Sample.ps 2926048 SPECIAL/24 SPECIAL VECTORĪll of the above files basically represent the same image but there are significant differences.
FILE NAME # OF BYTES # OF BITS PER PIXEL COMPRESSION RASTER OR VECTOR Bruce Boghosian of Boston University for the project Particle-in-Cell Simulation of Two-Dimensional Drift Turbulence in a Pure Electron Plasma Column. The example image was generated by Erik Brisson of the Scientific Computing and Visualization group at Boston University for Dr. To view the first three of these examples, you will probably need to use an outside image viewing application – web browsers can only display a limited number of formats, generally including JPEG, GIF and PNG.
The following list indicates the image file formats and sizes of a single image in a variety of different formats for comparison purposes – all of these images are at 800×600 resolution. For a comparison of 24 bit vs 8 bit color, view the following page (in 24 bit PNG and 8 bit GIF formats respectively) The color lookup table then specifies colors in the full 24 bit true-color representation but it is so small relative to a normal sized image that the space it takes up is negligible. Thus, each pixel only requires 8 bits (1/3 of the space) to represent it. Instead, each pixel is represented by a single number (for 8 bit images, a value from 0-255) which is an index into a color lookup table. Image formats such as GIF also, generally, do not directly specify colors in the manner shown above. Additionally, some image formats allow for a much smaller range of colors (example: GIF is an 8 bit format and allows for only 256 different colors to be present in any image). Most image formats, therefore, are compressed to shrink the size of the image. This, however, is a very simple way of representing an image and takes a very large amount of disk space. It is also shown as an enlarged image (in the GIF format since the PPM format shown can not be displayed by most web browsers) where each pixel is replicated as a 50×50 solid colored square. The following is a super-simple image definition (3×3 image in ascii PPM format- from upper left, black, medium red, full red, medium grey, medium green, full green, white, medium blue, full blue). In the right proportions, red, green, and blue can be combined to form black, white, 254 shades of grey, and a vast array of colors (16,777,216 colors total). The simplest representation of an image has each pixel specified by three 8 bit (24 bits total) color values (ranging from 0-255) defining the amount of red, green, and blue respectively in each pixel.
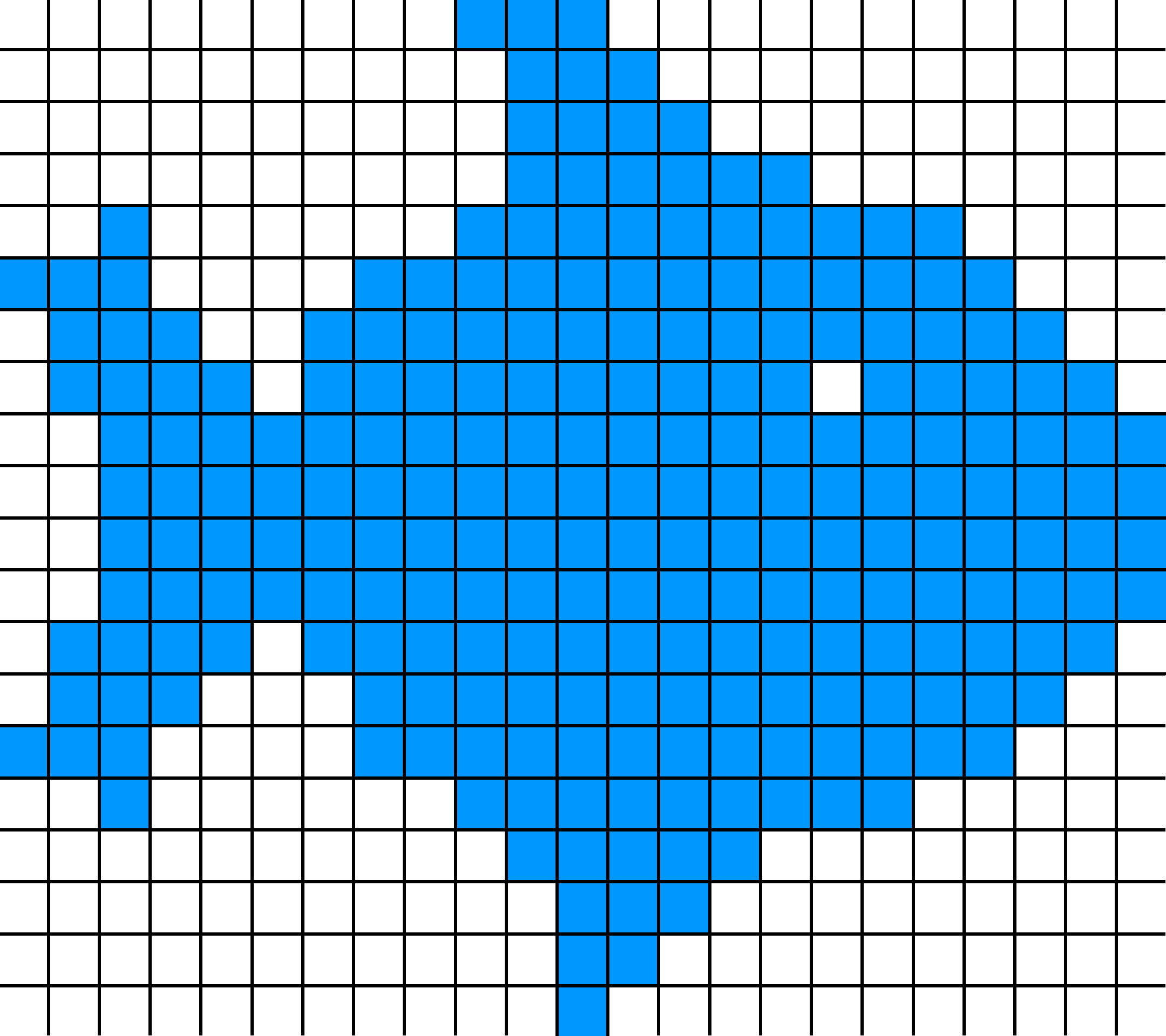
Each pixel (picture element) has one or more numbers associated with it, specifying a color which the pixel should be displayed in. A raster image file is a rectangular array of regularly sampled values, known as pixels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
